Gene expression transcription POGIL answers unveils the intricate dance between DNA, RNA, and proteins, guiding readers through the captivating journey of gene expression. This comprehensive resource delves into the stages of transcription, the factors that regulate it, and the innovative POGIL activities that illuminate these concepts.
Through a tapestry of clear explanations and engaging examples, this guide empowers students and educators alike to grasp the fundamentals of gene expression and transcription, unlocking the secrets of cellular communication.
Gene Expression and Transcription: Gene Expression Transcription Pogil Answers
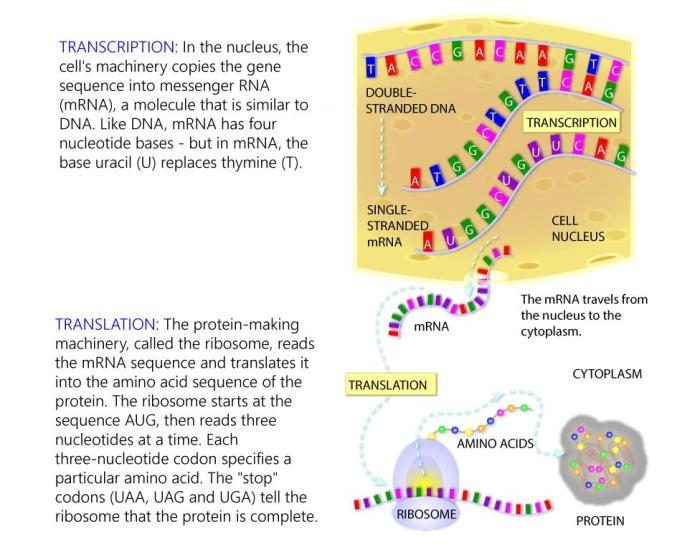
Gene expression is the process by which the information in a gene is used to direct the synthesis of a protein. The process of gene expression includes two main steps: transcription and translation.
Transcription
Transcription is the process of copying the information in a gene into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The mRNA molecule is then used to direct the synthesis of a protein. Transcription is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
Stages of Transcription
Transcription is divided into three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Initiation
Initiation is the process of finding the start site of a gene and beginning to synthesize the mRNA molecule.
Elongation
Elongation is the process of adding nucleotides to the mRNA molecule.
Termination
Termination is the process of stopping the synthesis of the mRNA molecule.
Factors that Regulate Transcription, Gene expression transcription pogil answers
Transcription is regulated by a number of factors, including promoters, enhancers, and repressors.
Promoters
Promoters are regions of DNA that are located near the start site of a gene. Promoters bind to RNA polymerase and help to initiate transcription.
Enhancers
Enhancers are regions of DNA that are located far from the start site of a gene. Enhancers bind to proteins called activators, which help to increase the rate of transcription.
Repressors
Repressors are proteins that bind to promoters and block the initiation of transcription.
POGIL Activities
Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) activities are a type of active learning activity that is designed to help students learn by doing. POGIL activities are typically based on real-world problems and require students to work in groups to solve the problem.
POGIL Activities for Gene Expression and Transcription
There are a number of POGIL activities that can be used to teach gene expression and transcription. These activities can be found online or in textbooks.
Examples of POGIL Activities
One example of a POGIL activity for gene expression is the “Gene Expression Simulation.” In this activity, students work in groups to simulate the process of gene expression. Students use a variety of materials, such as beads and pipe cleaners, to represent the different components of the gene expression process.Another
example of a POGIL activity for transcription is the “Transcription Puzzle.” In this activity, students work in groups to solve a puzzle that requires them to identify the different stages of transcription. Students use a variety of resources, such as diagrams and text, to help them solve the puzzle.
Answers to POGIL Questions
The following table contains answers to some common POGIL questions about gene expression and transcription.
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription? | RNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes mRNA molecules. | RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of a gene and begins to synthesize an mRNA molecule by adding nucleotides to the growing chain. |
| What are the three stages of transcription? | The three stages of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. | Initiation is the process of finding the start site of a gene and beginning to synthesize the mRNA molecule. Elongation is the process of adding nucleotides to the mRNA molecule. Termination is the process of stopping the synthesis of the mRNA molecule. |
| What are promoters? | Promoters are regions of DNA that are located near the start site of a gene. | Promoters bind to RNA polymerase and help to initiate transcription. |
Additional Resources
The following websites, articles, and videos provide additional information on gene expression and transcription.
- Gene Expression and Transcription: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/gene-expression-and-regulation/transcription-and-translation/a/gene-expression-and-transcription
- POGIL Activities for Gene Expression and Transcription: https://www.pogil.org/search?query=gene+expression
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA molecules by assembling nucleotides in a sequence complementary to the DNA template strand.
How do promoters regulate transcription?
Promoters are DNA sequences that bind RNA polymerase and other transcription factors, facilitating the initiation of transcription.
What is the difference between elongation and termination in transcription?
Elongation involves the addition of nucleotides to the growing RNA chain, while termination signals the end of transcription and the release of the newly synthesized RNA molecule.