A nurse is auscultating a client’s heart sounds, a crucial procedure that provides valuable insights into the health of the cardiovascular system. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance, techniques, and implications of auscultation, empowering nurses to effectively assess, interpret, and manage abnormal heart sounds.
Proper positioning of the stethoscope, identification of normal heart sounds (S1 and S2), and differentiation between innocent and pathological murmurs are key aspects of accurate auscultation. Understanding the causes and characteristics of abnormal heart sounds, such as clicks and gallops, enables nurses to recognize potential underlying cardiac conditions.
Assessment Techniques: A Nurse Is Auscultating A Client’s Heart Sounds
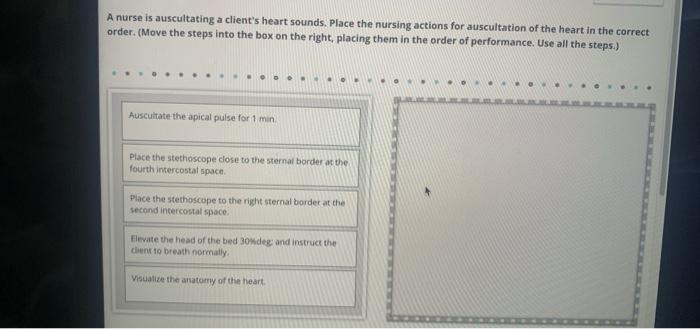
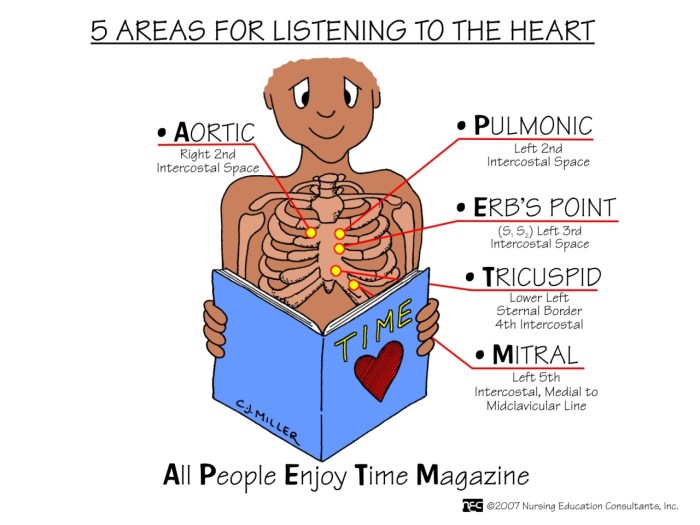
Auscultation is a critical technique for assessing heart sounds. Proper positioning of the stethoscope is essential for optimal sound acquisition. Place the diaphragm firmly against the chest wall, avoiding clothing or hair. Identify the four standard auscultation sites: the aortic area (second right intercostal space), the pulmonic area (second left intercostal space), the tricuspid area (fifth left intercostal space), and the mitral area (fifth left intercostal space, midclavicular line).
Identifying and Interpreting Normal Heart Sounds (S1 and S2)
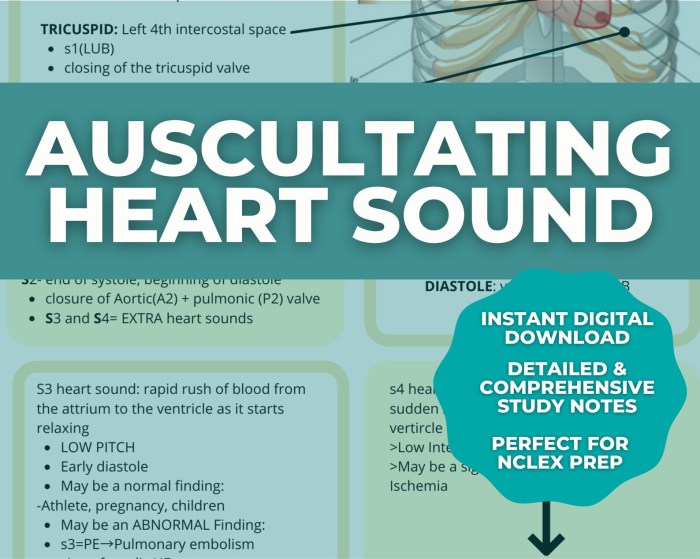
- S1 (first heart sound): A low-pitched, dull sound representing the closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves.
- S2 (second heart sound): A high-pitched, sharp sound representing the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
Abnormal Heart Sounds
Abnormal heart sounds can indicate underlying heart conditions. Common types include:
Murmurs, A nurse is auscultating a client’s heart sounds
- Innocent murmurs: Functional heart sounds that are not associated with heart disease.
- Pathological murmurs: Organic heart sounds that indicate structural abnormalities or disease.
Clicks
Sharp, high-pitched sounds that can indicate valvular stenosis.
Gallops
Extra heart sounds that can indicate impaired ventricular function.
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate documentation of heart sound findings is essential. Use a standardized template or table to organize and present findings in the medical record. Include the auscultation site, heart sounds heard (S1, S2, murmurs, etc.), and any additional observations.
Electronic health records (EHRs) facilitate the documentation and analysis of heart sound data. They allow for easy storage, retrieval, and sharing of patient information, enhancing communication among healthcare providers.
Nursing Interventions

Nurses play a vital role in monitoring and assessing heart sounds.
- Monitor heart sounds regularly, especially in patients with known heart conditions or at risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Administer medications as prescribed to manage abnormal heart sounds, such as diuretics for volume overload or antiarrhythmics for arrhythmias.
- Educate patients about the significance of heart sound monitoring and the importance of reporting any changes to their healthcare provider.
Collaboration with healthcare providers is crucial for interpreting and responding to abnormal heart sound findings. Nurses should communicate findings promptly and work with physicians to determine the appropriate course of action.
FAQs
What is the significance of auscultation in assessing heart sounds?
Auscultation allows nurses to evaluate the heart’s rhythm, rate, and presence of abnormal sounds, providing insights into the health and function of the cardiovascular system.
How can nurses differentiate between innocent and pathological murmurs?
Innocent murmurs are typically soft, short, and mid-systolic, while pathological murmurs are often louder, longer, and associated with specific heart conditions.
What is the role of electronic health records (EHRs) in auscultation?
EHRs facilitate the documentation and analysis of heart sound data, enabling efficient storage, retrieval, and sharing of information for improved patient care.