A traveling sinusoidal wave is described by the wave function, a mathematical equation that characterizes its properties. This wave, characterized by its amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and wave velocity, propagates through a medium, exhibiting wavefronts and wave rays.
The wave function provides insights into the wave’s behavior, enabling the determination of its properties. Wave propagation involves the transfer of energy without the physical displacement of the medium, influenced by factors such as the medium’s properties and the wave’s frequency.
1. Introduction: A Traveling Sinusoidal Wave Is Described By The Wave Function
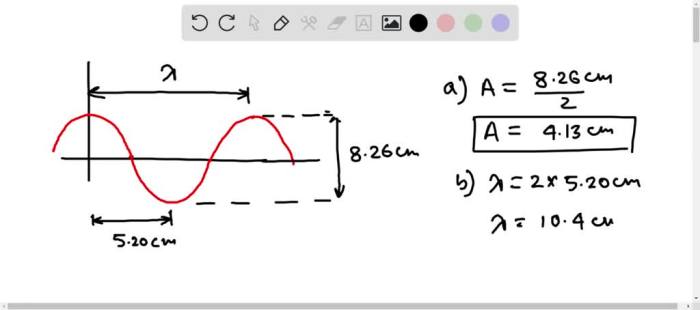
A traveling sinusoidal wave is a wave that propagates through a medium, exhibiting a sinusoidal variation in its amplitude over time and distance. It is characterized by its amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and wave velocity.
2. Wave Function
The wave function of a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by the equation:
$$y(x, t) = A \sin(kx
\omega t + \phi)$$
where:
- yis the displacement of the wave at position xand time t
- Ais the amplitude of the wave
- kis the wave number
- ωis the angular frequency
- φis the phase angle
3. Wave Propagation
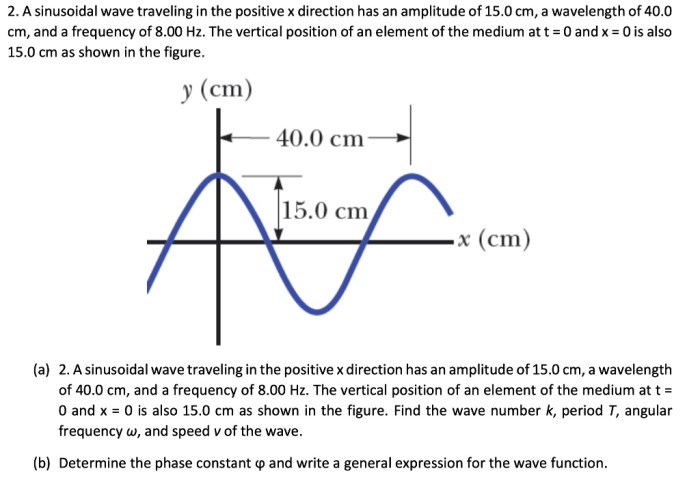
Wave propagation is the process by which a wave travels through a medium. The speed of wave propagation depends on the properties of the medium, such as its density and elasticity.
Wavefronts are surfaces of constant phase, while wave rays are lines that are perpendicular to wavefronts and indicate the direction of wave propagation.
4. Wave Interactions

Wave interactions occur when two or more waves meet. The different types of wave interactions include:
- Reflection: When a wave encounters a boundary, it can be reflected back into the medium from which it came.
- Refraction: When a wave passes from one medium to another, it can change direction due to a change in wave velocity.
- Diffraction: When a wave encounters an obstacle, it can spread out and bend around the obstacle.
- Interference: When two or more waves overlap, they can interfere with each other, resulting in constructive or destructive interference.
5. Wave Applications
Traveling sinusoidal waves have various applications in different fields, such as:
- Acoustics: Used in the design of musical instruments, soundproofing materials, and underwater acoustics.
- Optics: Used in the design of lenses, mirrors, and optical fibers.
- Telecommunications: Used in the transmission of radio waves, microwaves, and optical signals.
Q&A
What is the significance of the wave function in describing a traveling sinusoidal wave?
The wave function provides a mathematical representation of the wave, allowing for the determination of its properties, such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and wave velocity.
How does the wave function influence wave propagation?
The wave function governs the behavior of the wave as it propagates through a medium, determining its speed and direction of propagation.
What are the key factors that affect the speed of wave propagation?
The speed of wave propagation is influenced by the properties of the medium, such as its density and elasticity, as well as the frequency of the wave.