Cellular respiration yeast fermentation lab answers: Delve into the intricate processes of cellular respiration and yeast fermentation through a comprehensive lab investigation. This guide provides a step-by-step exploration of the key concepts, procedures, and data analysis involved in understanding these fundamental biological mechanisms.
Uncover the role of glucose in cellular respiration, the steps involved in the fermentation process, and the factors influencing fermentation rates. Engage in hands-on experimentation to collect and analyze data, gaining valuable insights into the cellular processes that sustain life.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration Yeast Fermentation Lab Answers

Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that converts glucose into energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The overall equation for cellular respiration is:
- C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2→ 6CO 2+ 6H 2O + energy (ATP)
The process of cellular respiration can be divided into three main steps:
- Glycolysis: This is the first step of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm. Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH.
- Krebs cycle: This step occurs in the mitochondria and involves the further breakdown of pyruvate into carbon dioxide, ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Electron transport chain: This step also occurs in the mitochondria and involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH 2to oxygen, which results in the production of ATP.
Yeast Fermentation
Yeast fermentation is a metabolic process that converts glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. It occurs in the cytoplasm of yeast cells and is used to produce alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine.
The overall equation for yeast fermentation is:
- C 6H 12O 6→ 2C 2H 5OH + 2CO 2
The process of yeast fermentation can be divided into two main steps:
- Glycolysis: This is the first step of yeast fermentation and is the same as the glycolysis step of cellular respiration. Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH.
- Ethanol fermentation: This step occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the conversion of pyruvate into ethanol and carbon dioxide. NADH is also oxidized to NAD+.
The rate of yeast fermentation is affected by a number of factors, including the temperature, the pH, and the concentration of glucose.
Lab Procedures
Materials:
- Yeast
- Glucose solution
- Beakers
- Thermometer
- pH meter
- Gas collection apparatus
Safety precautions:
- Wear gloves and a lab coat.
- Do not eat or drink in the lab.
- Keep all chemicals away from your face.
Procedure:
- Prepare a yeast suspension by adding 1 gram of yeast to 100 mL of water.
- Prepare a glucose solution by dissolving 10 grams of glucose in 100 mL of water.
- Set up a series of beakers, each containing a different concentration of glucose solution (e.g., 0%, 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5%).
- Add 10 mL of yeast suspension to each beaker.
- Incubate the beakers at a constant temperature (e.g., 30°C).
- Measure the pH of each solution at regular intervals.
- Collect the gas produced by the yeast fermentation using a gas collection apparatus.
- Measure the volume of gas produced at regular intervals.
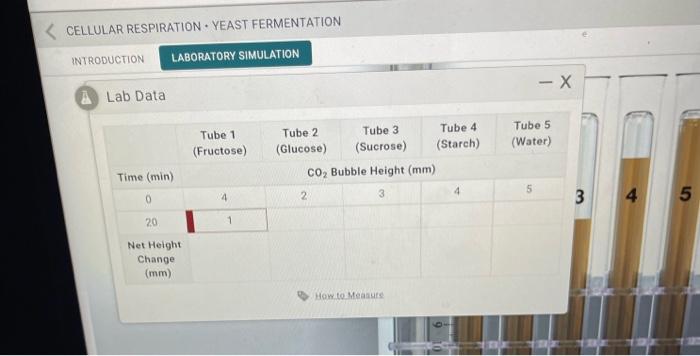
Data Analysis

The data collected from the lab can be used to create a line graph that shows the relationship between the fermentation rate and the glucose concentration.
The data can also be used to calculate the activation energy of yeast fermentation. The activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that is required for a reaction to occur.
Discussion
The results of the lab can be used to compare the rate of yeast fermentation at different glucose concentrations. The results can also be used to calculate the activation energy of yeast fermentation.
The findings of the lab can be used to understand the process of cellular respiration and fermentation. The findings can also be used to develop new methods for producing biofuels.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary role of glucose in cellular respiration?
Glucose serves as the primary energy source for cellular respiration, providing the necessary fuel for the metabolic processes that generate ATP.
How does yeast convert glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide during fermentation?
In the absence of oxygen, yeast undergoes fermentation, converting glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide as byproducts through a series of enzymatic reactions.
What factors can affect the rate of fermentation in yeast?
The rate of fermentation is influenced by factors such as glucose concentration, temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors or activators.